LEED certification is essential for federal buildings to meet energy efficiency, water conservation, and sustainability goals. Federal projects must achieve at least LEED Silver certification, ensuring eco-friendly practices in design, construction, and operations. Here’s what you need to know:
- What is LEED? A green building framework by USGBC, focusing on energy, water, materials, air quality, and site sustainability.
- Certification Levels: Ranges from Certified (40 points) to Platinum (80+ points).
- Key Focus Areas: Site planning, energy efficiency, renewable materials, and healthier indoor environments.
- Benefits: Lower operating costs, healthier workspaces, and compliance with federal sustainability mandates.
- Process: Register projects, submit detailed documentation, and undergo a two-phase review.
LEED-certified federal buildings deliver measurable cost savings, improved employee well-being, and long-term value. Start early, plan carefully, and align efforts with federal sustainability goals.
LEED Certification Basics
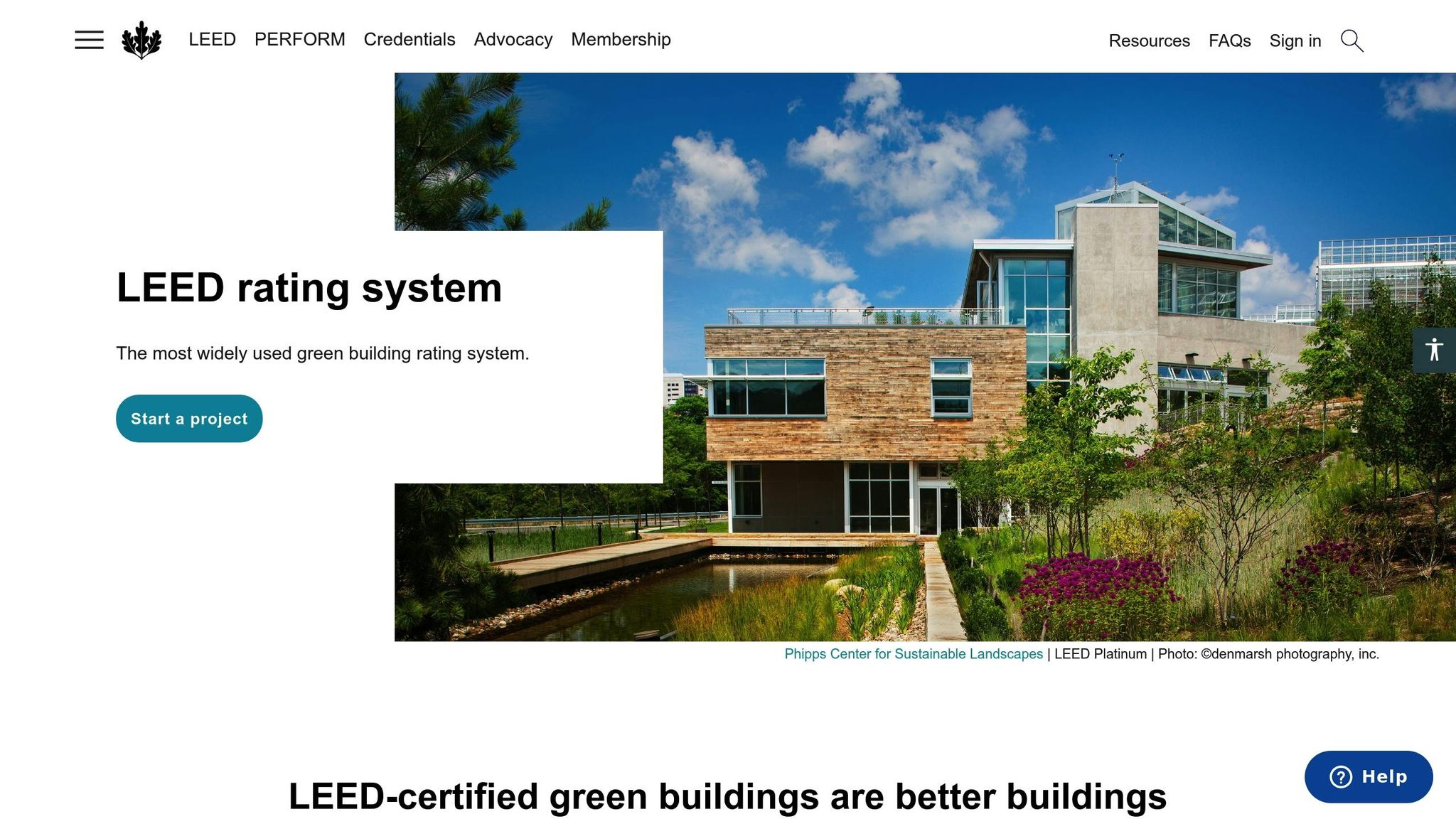
What is LEED?
LEED, created by the US Green Building Council (USGBC), provides a framework for designing buildings that are efficient, environmentally friendly, and promote healthier living. It uses a points-based system to evaluate and reward sustainable practices across several key areas.
The system focuses on performance in seven main categories:
- Sustainable Sites
- Water Efficiency
- Energy and Atmosphere
- Materials and Resources
- Indoor Environmental Quality
- Innovation in Design
- Regional Priority
To fully understand LEED, it’s important to know how its rating system works.
4 LEED Rating Levels
LEED certification is awarded at four levels, based on the total points a building earns for its sustainable design and construction efforts:
| Certification Level | Points Required |
|---|---|
| Certified | 40–49 points |
| Silver | 50–59 points |
| Gold | 60–79 points |
| Platinum | 80+ points |
Each level reflects a stronger commitment to sustainability. These benchmarks are often used to guide federal projects in meeting environmental goals.
Guiding Principles and Third Party Certification
LEED Requirements for Federal Buildings
Federal LEED certification focuses on three main areas, each outlining specific performance standards for federal projects.
Site Planning and Water Use
This area emphasizes reducing stormwater runoff through effective capture systems, using water-efficient fixtures, and implementing smart irrigation methods. It also encourages selecting sites that are either already developed or close to public transportation.
Energy Use and Materials
Federal projects must prioritize energy-efficient designs, incorporate renewable energy sources, and use materials that are recycled, locally sourced, or environmentally responsible. These practices align with federal sustainability objectives.
Indoor Air Quality
To ensure healthier indoor environments, federal buildings must meet strict standards for ventilation, use low-emission materials, and maintain controlled thermal conditions. Access to natural light is also a priority to create productive and comfortable spaces.
Federal LEED Requirements
Federal agencies incorporate LEED certification into construction and renovation projects to promote sustainable practices.
Federal Building Standards
Federal projects, whether new, renovated, or modernized, follow LEED guidelines tailored to specific needs. While requirements can differ by project, the focus consistently remains on areas like energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste management. These standards help shape and align with evolving federal policies.
Current Policy Requirements
Recent federal initiatives strengthen efforts to reduce environmental impact. Agencies are tasked with pursuing net-zero emissions and optimizing energy and water use. Regular monitoring and reporting ensure progress toward long-term sustainability goals.
LEED-certified projects must include features like advanced metering, renewable energy solutions, and waste reduction strategies. Additionally, life-cycle cost analysis is used to ensure projects deliver long-term value for taxpayers.
sbb-itb-8737801
LEED Benefits for Federal Buildings
Meeting federal LEED requirements does more than check a box – it provides measurable advantages.
LEED-certified federal buildings experience lower operating costs and create healthier spaces for employees.
Cost and Resource Savings
These buildings cut expenses by improving the efficiency of energy, water, and lighting systems, leading to long-term savings.
Healthier Work Environments
Features like better ventilation, low-emission materials, natural light, and sound management contribute to reduced health risks and improved employee productivity.
Supporting Federal Mandates
LEED certification helps federal agencies comply with goals for energy efficiency, carbon reduction, and sustainable building practices by offering clear performance metrics.
Getting LEED Certified
Earning LEED certification requires careful planning and adherence to specific steps. Here’s how to navigate the process effectively.
Project Setup
Start by registering your project on the USGBC online portal. This step lays the foundation for a smooth certification journey. Here’s what you need to do:
- Choose the right LEED rating system for your building type.
- Put together a team with LEED expertise.
- Develop a preliminary scorecard and timeline that aligns with federal procurement schedules.
Designate a LEED Project Administrator to handle documentation and coordination throughout the process.
Required Documents
Thorough documentation is essential for securing LEED certification. You’ll need to provide:
- Building design and construction specifications
- Energy modeling reports and calculations
- Documentation on water efficiency measures
- Materials and resources tracking sheets
- Indoor environmental quality test results
- Site sustainability information
- Commissioning reports
Submit all required documents through the LEED Online platform, following USGBC’s guidelines. Federal agencies should also maintain detailed records for potential recertification down the line.
Review Process
1. Preliminary Review
The initial review typically takes 30–40 business days. During this phase, you’ll receive feedback on credit compliance and have the chance to address any issues.
2. Final Review
This step involves reviewing any additional documentation you provide. It usually takes 20–25 business days and results in the confirmation of your certification level.
3. Optional Appeal
If there are contested credits, you can file an appeal. This requires a review fee and takes about 25 days.
Make sure to align the review timelines with your fiscal planning cycles to avoid delays.
Common LEED Certification Issues
Achieving federal LEED certification comes with challenges that demand careful planning and budgeting.
Cost Planning
Managing costs is one of the biggest challenges in the LEED certification process. Expenses like certification fees, documentation, energy modeling, commissioning services, and system upgrades can vary widely based on the project’s size, scope, and complexity. To handle these costs effectively:
- Build LEED requirements into the project’s initial specifications to avoid costly changes later.
- Set aside part of the construction budget specifically for certification-related expenses.
- Consider long-term savings to offset the upfront investment.
- Include certification costs in your organization’s annual budget planning.
In addition to financial considerations, variations in building design and team preparation add further complexity.
Building Type Differences
The type of building significantly impacts the certification process. New construction projects typically allow more flexibility to incorporate sustainable strategies, while existing buildings often face unique constraints.
For new construction, it’s beneficial to:
- Plan for sustainability from the project’s outset.
- Use opportunities to aim for higher certification levels.
- Choose sustainable materials and design systems with flexibility in mind.
For existing buildings, the challenges are different and may include:
- Limited ability to modify the building’s structure.
- Restrictions due to historical preservation requirements.
- Challenges posed by ongoing occupancy.
- Complications in retrofitting existing systems.
Staff Training Needs
A knowledgeable team is critical for navigating LEED certification. Training should focus on areas like obtaining LEED credentials, mastering federal procurement processes, energy modeling, and adopting sustainable operational practices.
To support this, consider the following:
- Assign a dedicated LEED coordinator for each project.
- Implement strong documentation and tracking systems.
- Schedule regular training sessions to keep the team updated.
- Develop standard procedures that promote sustainability.
Budgeting for training, including certifications and continuing education, is just as important as planning for the certification itself. Regular refresher courses can help your team stay aligned with evolving LEED standards.
Conclusion
LEED certification plays a key role in helping federal buildings align with sustainability goals while achieving measurable outcomes. This guide highlights the importance of considering the entire building lifecycle – planning, construction, and operations – when pursuing certification.
Successfully navigating the LEED certification process requires careful planning, sufficient resources, and expert input. Federal agencies should address both the immediate certification needs and the broader benefits of maintaining sustainable operations.
To achieve the best results, sustainable practices should be incorporated from the initial design phase through ongoing operations. As outlined in the project setup and review process, these practices are essential for optimizing long-term building performance.
With evolving sustainability standards and emerging technologies, a continued focus on LEED practices ensures that federal buildings remain efficient and healthy. Investing in certification today lays the groundwork for facilities that meet environmental goals while supporting operational success.
Related posts
- How will Trumps Exec. Orders affect your Federal Sales?
- How to Track GSA Contract Compliance
- Top 5 Compliance Issues in GSA Contracts
- How GSA Contracts Impact Federal Construction Compliance


